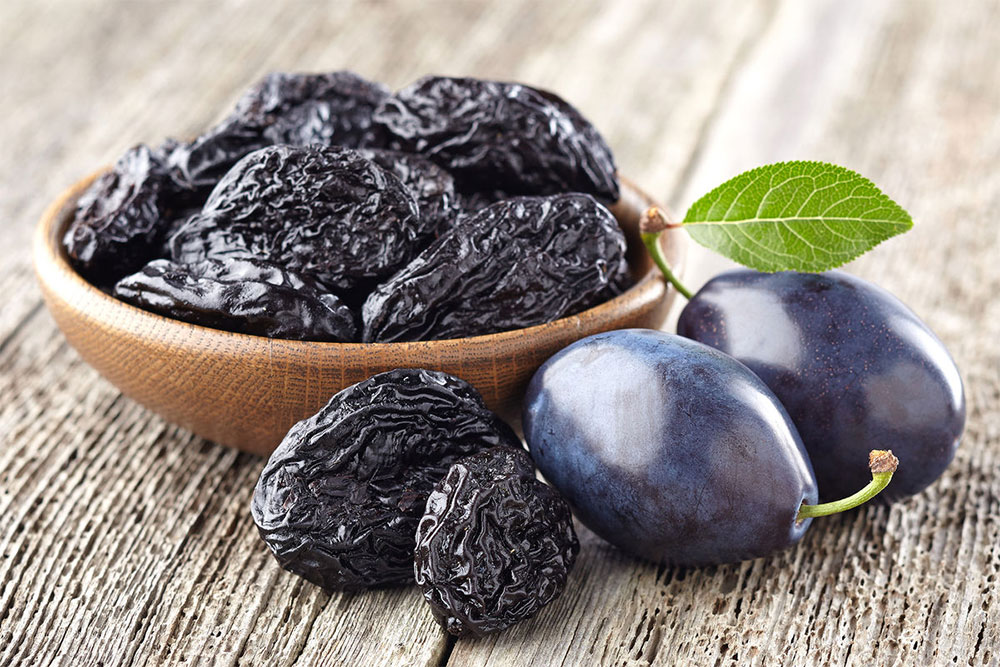
Prunes, or dried plums, have long gained recognition due to their unique taste and numerous beneficial properties. This nutritious product is rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals and antioxidants, making it a valuable addition to a healthy diet. Regular consumption of prunes helps improve digestion, support the cardiovascular system, strengthen bones and regulate blood sugar levels. Prunes are not only delicious, but also have many healing properties that help support overall health and well-being.
Composition of prunes
Prunes, as a dried fruit, have a rich and varied nutritional composition, which includes many vitamins, minerals and other beneficial substances. Here are the main components of prunes:
Vitamins
- Vitamin A (beta-carotene): important for vision, immune system and skin health.
- Vitamin K: essential for blood clotting and bone health.
- B vitamins (B1, B2, B3, B6): important for energy metabolism, nervous system and skin health.
- Vitamin C: antioxidant that supports the immune system (in smaller quantities).
Minerals
- Potassium: essential for maintaining normal blood pressure and muscle function.
- Magnesium: is involved in hundreds of biochemical reactions in the body, including the regulation of muscle and nerve function.
- Phosphorus: important for healthy bones and teeth.
- Calcium: essential for healthy bones and teeth.
- Iron: important for the formation of hemoglobin and the transport of oxygen in the blood.
- Zinc: important for the immune system and wound healing.
- Copper: Essential for the formation of red blood cells and maintaining vascular health.
Dietary fiber
- Prunes are rich in soluble and insoluble fiber, which help improve digestion and maintain gut health.
Antioxidants
- Phenolic compounds: powerful antioxidants that help protect cells from free radical damage.
Sugar
- Contains natural sugars such as glucose and fructose, which provide a quick source of energy.
Organic acids
- Sorbitol: a natural sugar alcohol that has a laxative effect and helps improve digestion.
Nutrient content in 100 grams of prunes:
- Calories: about 240 kcal
- Proteins: 2.2 g
- Fats: 0.4 g
- Carbohydrates: 63.9 g (of which sugars: 38.1 g)
- Dietary fiber: 7.1 g
- Potassium: about 732 mg
- Vitamin A: 781 IU (International Units)
- Vitamin K: 59.5 mcg
- Iron: 0.93 mg
This rich composition makes prunes not only tasty, but also an extremely healthy product that can maintain and improve health when consumed regularly.
What are the benefits of prunes
What are the benefits of prunes? Prunes have many beneficial properties due to their rich nutritional composition. Here are the main health benefits of prunes:
- Prunes are rich in dietary fiber, which helps improve digestion and prevent constipation. It contains natural laxatives such as sorbitol and diphenylisatin, which promote regular bowel function.
- Prunes contain high amounts of antioxidants, such as phenolic compounds, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. This may reduce the risk of chronic diseases, including heart disease and cancer.
- Prunes are rich in potassium and vitamin K, which are important for bone health. Research shows that regular consumption of prunes may help prevent bone loss and reduce the risk of osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women.
- Despite their sweetness, prunes have a low glycemic index, which means they slowly raise blood sugar levels. This makes it a good choice for people with diabetes or those watching their blood sugar levels.
- The potassium found in prunes helps regulate blood pressure, and the antioxidants help lower levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL). These properties may help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
- Prunes are a good source of B vitamins, vitamin A, iron, magnesium and manganese. These nutrients are important for metabolism, energy, skin health and the immune system.
- Due to their high fiber content, prunes can promote feelings of fullness, which helps control appetite and promote healthy weight loss.
Prunes can be consumed in their pure form, added to baked goods, porridges, salads, or used in cooking to make sauces and desserts. Its regular consumption in moderate quantities can significantly contribute to improving overall health.
Who shouldn’t eat prunes
Although prunes are healthy for most people, there are certain groups that should be careful or avoid eating them:
- People with diabetes
Prunes contain high amounts of natural sugars and carbohydrates, which can lead to high blood sugar levels. People with diabetes or insulin resistance should consume prunes with caution and in moderation, while monitoring the food’s glycemic index.
- People with allergies
Although allergy to prunes is rare, it is possible. Symptoms may include skin rash, itching, swelling, difficulty breathing and other allergic reactions. If you are allergic to plums or other stone fruits, you should avoid prunes.
- People with sensitive digestion
Prunes are high in sorbitol, a natural sugar alcohol that can cause bloating, gas and diarrhea, especially in people with sensitive gut or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). People with these conditions should limit their consumption of prunes.
- People with kidney problems
Prunes are rich in oxalates, which may contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible people. If you have a history of kidney stones, you may want to limit your consumption of prunes and consult your doctor.
- People taking certain medications
Prunes contain vitamin K, which can affect blood clotting. People taking anticoagulants (such as warfarin) should be careful with the amount of prunes they consume and consult a doctor about safe dosage.
- Children and babies
Prunes and their juice may be useful in relieving constipation in children, but they should not be given to infants without consulting a pediatrician. The high sugar content and laxative properties may be too strong for young children.
If you have any of these conditions or are unsure about eating prunes, it is best to consult with your doctor or nutritionist to determine if it is safe to include this product in your diet.